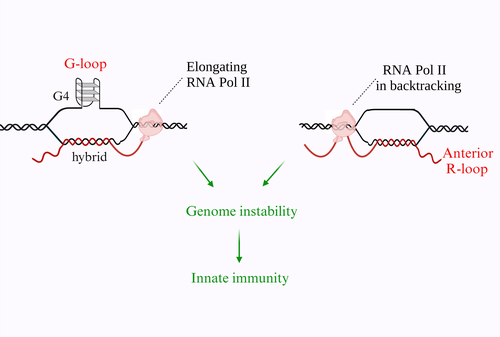
G-loop and anterior R-loop can form in living human cells leading to genome instability and activation of innate immune gene expression.
Research Themes
Regulation of genomic functions is a complex process that involves several protein factors and nucleic acid structures. Thanks mainly to the development of parallel sequencing technologies (known as Next Generation Sequencing, NGS), it has become possible to investigate how particular secondary structures of nucleic acids can affect fundamental genomic functions such as gene expression, DNA replication, genome recombination and stability. Non-B DNA structures have been established to play major roles in cell transformation and neuron degeneration as they markedly influence expression profiles and genome stability. In this context, our research focuses on how non-B DNA structures affect chromatin organization, genome functions and stability, on one side, and how they are regulated by DNA topoisomerases, on the other.
We are particularly interested in R loops and G-quadruplex (G4). R-loops are formed during transcription upon re-annealing of the nascent RNA to the DNA template strand, forming an RNA:DNA hybrid and forcing the non-template strand to loop out in a single-stranded status. G4s are instead generated by single-stranded guanine-rich DNA sequences that fold into stable four-stranded structures wherein three sets of four guanines are arranged in three stacking planar quartets. R loops and G4s are DNA structures particularly sensitive to DNA supercoilings. Negative DNA supercoils generated behind an elongating RNA polymerase are thought to facilitate R-loop formation by inducing an underwound DNA duplex favorable to re-annealing of the nascent transcript to its template. Interestingly, human genomic maps showed that active promoters are free of nucleosomes, have more negative supercoils than other genomic sites, and are regions where R loops and G4s can form more easily. DNA Topoisomerase I is a main cellular factor controlling topological homeostasis of the genome. Thus, we have studied the role of Topoisomerase I in R loop formation in human cells by siRNA gene silencing or using specific inhibitors of Top1 religation activity. The findings were somewhat surprising as they demonstrate that Topoisomerase I can indeed regulate an R-loop, but it can either favor or dis-favor its formation depending on chromatin context.
We recently investigated the role of anticancer TOP1 poisons in micronuclei generation, leading to activation of the cGAS-STING pathway and immune gene expression in cancer cells. In addition, we show that Top1 poisons can activate both IRF3- and NF-kB-dependent genes, however, they cannot in SCLC cancer cells as the cGAS-STING pathway is markedly impaired likely due to several mechanisms including a drastic reduction of STING and/or cGAS expression.
We also focus in defining if chemical stabilization of G4 can trigger the formation of R-loops in living cells. We performed several experiments to investigate the effects of G4 ligands on R-loop formation and genome integrity in human cancer cells using R-loop immunoprecipitation methods (called DRIP) and NGS technology. G4 ligands induce an immediate increase of nuclear R loops as G4s and R-loops can cooperate and stabilize each other during transcription, forming a G-loop. Moreover, the data show that DNA damage induced by G4 ligands are mediated by R-loops.
In summary, our research goal is to establish molecular and epigenetic mechanisms dependent on non-B DNA structures of transcription regulation and genome instability.
For more information, please visit our website.
